Introduction
In this article, we will discuss a common challenge i’ve face many times in Kubernetes: Troubleshooting n8n WebSocket Issues on NGINX Ingress. WebSockets are widely used in modern applications to maintain persistent, real-time connections. However, when using an NGINX Ingress Controller, WebSocket connections often fail if the ingress configuration is incomplete or misaligned with the specific controller version being used. This article aims to provide some explanation of the issue, why it happens, and how to fix it in a Kubernetes environment using the official NGINX Inc. ingress controller.
This article was prepared on an environment deployed with Kuberspray. If you want to have such an environment too, go to How to Deploy Kubernetes Using Kubespray
Procedure
The problem was showed in n8n as Connection Lost
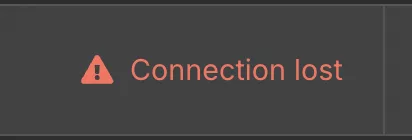
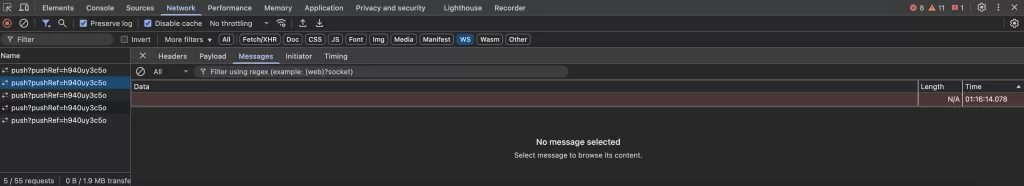
And you could see errors in the Developer Tools
Background & Root Cause
In our scenario, an application (n8n) that utilizes WebSockets was deployed behind the NGINX Ingress Controller. The WebSocket functionality worked correctly when accessed via kubectl port-forward, but failed when accessed externally through the ingress.
After investigation, the root cause was identified as a configuration mismatch:
- The Kubernetes cluster was using the NGINX Inc. official ingress controller (
nginx/nginx-ingress), deployed via Helm. - The ingress resource annotations used were from the community ingress-nginx project (
kubernetes/ingress-nginx), such as:nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeoutnginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/configuration-snippetnginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/websocket-services
- These annotations are not supported by the NGINX Inc. ingress controller and were silently ignored.
- Additionally, the ingress controller was deployed with the
-enable-snippets=falseflag, disabling any custom snippet injection. - This caused WebSocket upgrade headers (
Connection: upgrade,Upgrade: websocket) to be dropped, breaking the connection.
A common confusion between the two NGINX Ingress projects contributed to the issue:
| Community ingress-nginx | NGINX Inc. ingress controller (F5 version) |
|---|---|
Repo: kubernetes/ingress-nginx | Repo: nginx/nginx-ingress |
Uses annotations: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/* | Uses annotations: nginx.org/* |
| Snippets enabled by default | Snippets require -enable-snippets=true |
| Widely used in OSS environments | Often used in commercial NGINX deployments |
Avoid Tunnel Vision
While investigating, I was sure the issue was with the application. In order to refute that, I’ve used kubectl port-forward to check see Kubernetes’ guide for port-forward :
$ kubectl port-forward --address 0.0.0.0 svc/n8n 9999:80Then connected to the n8n website with the address of the machine where I ran the kubectl command to see if it worked, and it did. Meaning the application wasn’t the issue, the nginx ingress was.
How to Solve
The issue was resolved by applying the correct NGINX Inc. annotations and removing the unsupported ones.
Change community ingress annotations and apply NGINX Inc. specific annotations
Annotations like nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/* were updates with nginx.org to have effect.
The following annotations were used:
nginx.org/proxy-read-timeout: "3600"
nginx.org/proxy-send-timeout: "3600"
nginx.org/websocket-services: "n8n-service"Ensure correct ingress path rule
The WebSocket endpoint /rest/push was correctly routed in the ingress resource:
paths:
- path: /rest/push
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: n8n-service
port:
number: 5678WebSocket Testing
After configuration, WebSocket functionality was tested using websocat on macOS:
$ brew install websocat
$ websocat wss://your-domain.com/rest/pushA successful connection confirmed that the issue was resolved.
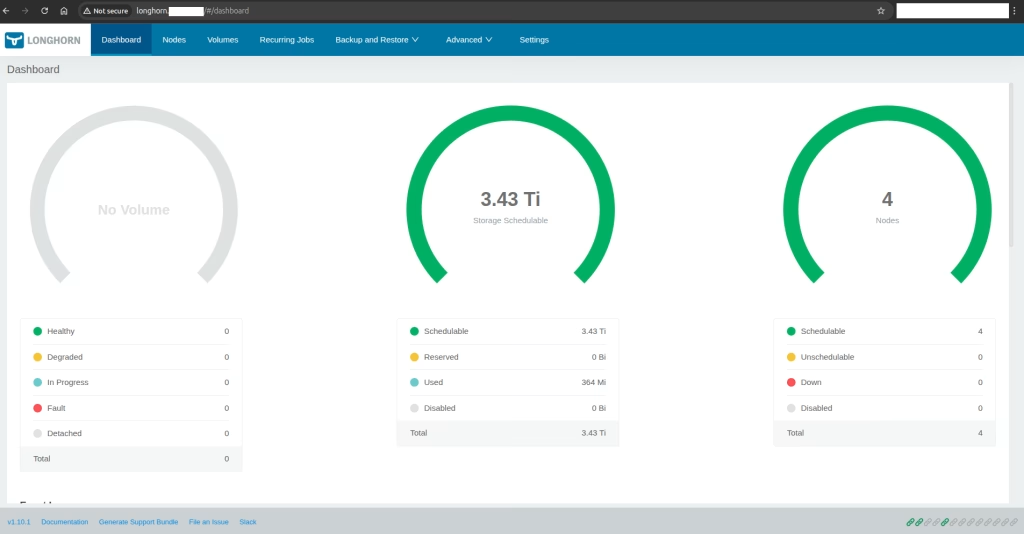
Now you can see in the application that it works
Why port-forward worked?
The WebSocket connection worked via kubectl port-forward because it bypassed the ingress controller entirely, connecting directly to the application pod without requiring proxy headers or configuration.
Summary
In this article, we examined the problem of Troubleshooting n8n WebSocket Issues on NGINX Ingress and detailed its root cause and solution. The issue stemmed from the confusion between the NGINX community ingress controller and the official NGINX Inc. ingress controller, leading to misapplied annotations and configuration. By applying the correct nginx.org/* annotations and testing with a WebSocket client, the problem was successfully resolved. Understanding the subtle but critical differences between ingress controllers is essential to avoid similar issues in Kubernetes environments.